Difference between revisions of "Dichotomy"
m (moved The two domains to Dichotomy over redirect) |
(onlyinclude) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{glossary}} | + | {{glossary}}<onlyinclude>The [[nodal model]] is founded on what could be called a ''meta-dichotomy'', or a dichotomy of dichotomies which we'll call ''dichotomy'' and ''duality''. Both are recursive and so in a sense give rise to a discrete division process implying two kinds of ''continuous dimension''. The ''dichotomy'' dimension is the kind which have opposites at each end like ''black'' and ''white'' or ''negative'' and ''positive'', and they concern sequence, order and time. This dimension is thought of as "horizontal" because both ends are equally powerful and part of the same domain. |
| − | The [[nodal model]] is founded on what could be called a ''meta-dichotomy'', or a dichotomy of dichotomies which we'll call ''dichotomy'' and ''duality''. Both are recursive and so in a sense give rise to a discrete division process implying two kinds of ''continuous dimension''. The ''dichotomy'' dimension is the kind which have opposites at each end like ''black'' and ''white'' or ''negative'' and ''positive'', and they concern sequence, order and time. This dimension is thought of as "horizontal" because both ends are equally powerful and part of the same domain | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The ''duality'' kind of dimension is about ''containment'' like ''foreground and background'' and it forms the "vertical" dimension of hierarchy. It's been called ''duality'' because its the kind of dichotomy that gives rise to the [[w:Wave-particle duality|wave-particle duality]] where one is the environment and the other an object within it. Some more abstract ones are ''subject/object'', ''potential/actual'' and ''field/point''.</onlyinclude> | ||
== The two domains in binary == | == The two domains in binary == | ||
A binary ''word'' is a sequence of binary digits of a given length. A binary ''space'' is the set of all distinct binary words of the same length. Each of these binary words represents a unique location which exhibits a ''state''. The state is a binary word of the same size as the address. So for example if we have a 10-bit binary space, then we effectively have a set of 1024 locations, each containing a 10-bit value. Since the addresses and values are the same size, values can represent addresses. | A binary ''word'' is a sequence of binary digits of a given length. A binary ''space'' is the set of all distinct binary words of the same length. Each of these binary words represents a unique location which exhibits a ''state''. The state is a binary word of the same size as the address. So for example if we have a 10-bit binary space, then we effectively have a set of 1024 locations, each containing a 10-bit value. Since the addresses and values are the same size, values can represent addresses. | ||
Revision as of 06:41, 13 August 2011
The nodal model is founded on what could be called a meta-dichotomy, or a dichotomy of dichotomies which we'll call dichotomy and duality. Both are recursive and so in a sense give rise to a discrete division process implying two kinds of continuous dimension. The dichotomy dimension is the kind which have opposites at each end like black and white or negative and positive, and they concern sequence, order and time. This dimension is thought of as "horizontal" because both ends are equally powerful and part of the same domain.
The duality kind of dimension is about containment like foreground and background and it forms the "vertical" dimension of hierarchy. It's been called duality because its the kind of dichotomy that gives rise to the wave-particle duality where one is the environment and the other an object within it. Some more abstract ones are subject/object, potential/actual and field/point.
The two domains in binary
A binary word is a sequence of binary digits of a given length. A binary space is the set of all distinct binary words of the same length. Each of these binary words represents a unique location which exhibits a state. The state is a binary word of the same size as the address. So for example if we have a 10-bit binary space, then we effectively have a set of 1024 locations, each containing a 10-bit value. Since the addresses and values are the same size, values can represent addresses.
In such a space, we already have the two domains at play with addresses (unchangeable), each paired with a value (changeable). But the two domains come into play far more strongly when we introduce the concept of sequence into the structure. By introducing a successor operation, every location is given two unique neighbours. This is the basis of interpreting the binary word as a unique number and the whole set of possible words of that length as a dimension (actually a loop because the successor of 111 is 000).
This idea of dimension is derived from interpreting a binary word as a sequence and reading it from one end to the other to yield a specific location. But here's where the two domains come into play, because the successor process on which this interpretation is built is actually geometric in nature, and as such, comes with a geometric complement. The complementary interpretation is multiplexing and is obtained by reading the address sequence the other way (reverse addressing; see FFT for more detail about this reversal).
Dimension and multiplexing are isomorphic with the two domains because forward addressing yields a linear "location" space, and reverse, yields the energy distribution, or "executional focus" over the entire space. Or to say it in a more dichotomous way, forward addressing divides the space into a sequence of locations and reverse addressing divides the focus (one point-of-view) into many foci (many parallel points of view). Forward is division of object or state, and reverse, division of subject.
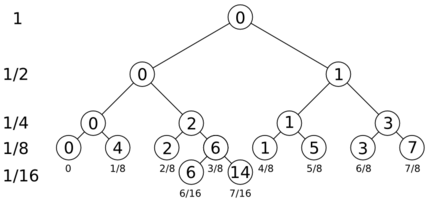
The following diagram shows how the single binary digit representing "1" (the unified undivided Whole) can be split in such a way as to create an infinitely-divisible continuum both spatially and temporally.
The tree can divide into any number of levels; here three levels are shown, with a single node dividing down one level further as an example. The meaning of the numbers in the diagram are as follows:
- The numbers down the left hand side show what proportion of the whole each item in that layer represents.
- The numbers below the nodes show the numeric value of the node by summing each rightward branch starting from root
- The numbers inside the node represent the order in which the nodes are visited in multiplexed order starting at zero
Starting with 1 at the top level and halving the value down each successive layer allows any level to divide to any depth without repeating values from higher levels and disrupting the continuum.
Heaven & Earth
Let's have a closer look at the eix formular to see how it splits by odd and even into the two domains. First here's its taylor-series expansion (I've separated the i and x powers out for clarity - see also the local e article)...
Now because i2 is -1, successive powers of i lead to the terms alternating between real and imaginary as follows...
As you can see, all the terms have become a sequence of alternating positive and negative i or 1, so this means we can separate all the terms containing i and factorise them out,
And so you can see that all the even terms have grouped together to make the real component, and all the odds make the imaginary, so where x is angular, eix yields the rectangular components, hence:
or more generally, when e is raised to the power of any arbitrary complex number,