Difference between revisions of "Process a scanned diagram"
m |
|||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
== Change colour of selected areas of text == | == Change colour of selected areas of text == | ||
| − | [[Image:Example-diagram- | + | [[Image:Example-diagram-5.png|right]] |
Sometimes its useful to convert some of the text to a different colour again. In this example we'll convert | Sometimes its useful to convert some of the text to a different colour again. In this example we'll convert | ||
some of the words to green and use the [[MW:Extension:ImageMap|Image map extension]] to make the green words | some of the words to green and use the [[MW:Extension:ImageMap|Image map extension]] to make the green words | ||
Revision as of 05:58, 8 July 2008
| Process a scanned diagram Organic Design procedure |
Here's an example of a scanned diagram which will serve to show the effect of each processing step. These instructions apply to GIMP.
Contents
Discard redundant colour information
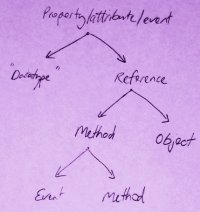
If the image has no useful colour information such as in the case of a white-board diagram or pencil/pen diagrams, convert the image to greyscale from the image/mode menu. This step will make the converted results more consistent, and will increase compression efficiency. The image to the right demonstrates the removal of the colour information from our example image.
Adjust the contrast attributes
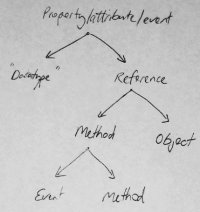
Usually the scanned image will not range from complete black to white and may have inconsistent shading. The main tools for handling this are Brightness-contrast, Levels and Curves, all in the Colors menu. Brightness-contrast is the most basic and easilt understandable, Levels is good for ensuring that the image fills the range properly from black to white, and Curves (my personal favourite) allows direct visual control over the transformation from current brightness range to target range. All the tools offer a preview which may have to be ticked to enable. The curves were adjusted on our example image yielding the image to the right.
Make the background transparent
We can't be sure that the image will always be used on a white background, so its best if it's given transparency and saved in PNG format. Unfortunately IE browsers before version 7 require JavaScript hacks to allow PNG's to render with transparency.
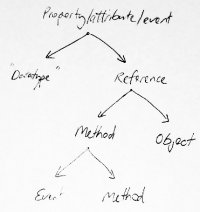
The most accurate way of converting the image from white-to-back to transparent-to-black without any loss of information is to convert the greyscale channel to a selection, fill the selection black in a new layer, then discard the original background layer. To convert the greyscale channel to a selection, bring up the channels dialog, right-click on the channel named "grey" and select Channel to selection. GIMP will render the transparency as a chequer pattern as shown in the image to the right.
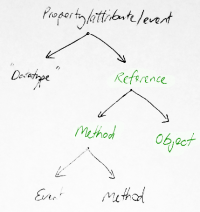
Change colour of selected areas of text
Sometimes its useful to convert some of the text to a different colour again. In this example we'll convert some of the words to green and use the Image map extension to make the green words into links.
First we'll need to convert the image from greyscale back to RGB from the Image/Mode menu. Next ensure the transparency is locked in the layers dialog, then simply paint over the areas with the appropriate brush and colour, with the transparency locked, only the black will be affected, not the background.
Resize and upload the image
Most in-wiki images don't need to be larger than the screen or the size they'll be used at, but an exception would be when the detail of high resolution is required, or when the image may be used for printing purposes, but most often such images don't belong in the wiki.
Resize the image in Image/Scale then export as a PNG, and upload it into the wiki.