Google Maps
This was job which I did at the beginning of 2012 for Trail WIKI, I'm documenting it here because it involved many different interesting aspects and also included some useful information which will help with later jobs.
The wiki contains many pages which represent hiking trails. It uses an infobox template so that various information about each trail such as its distance, elevation and other attributes can be contained in a structured way in the article.
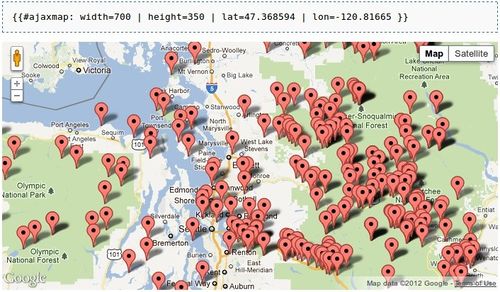
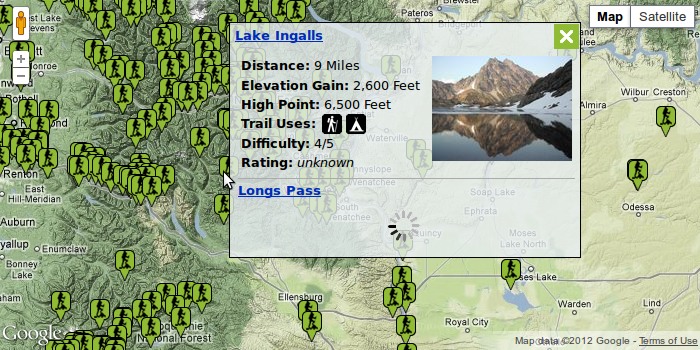
On the main page is a Google map which has markers for all the trails, and when one is clicked a popup is revealed containing a link to the associated trail article.
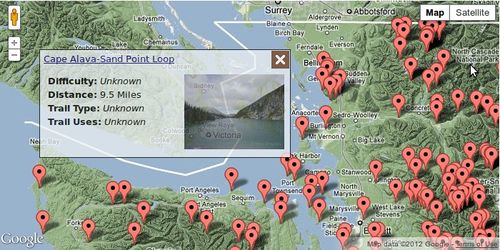
The client wanted to have this map functionality extended such that the infobox that pops up is customised to the style of the site and contains some of the key information from the trail article's infobox. Also he wanted to use the Semantic Maps extension so that he could have other maps throughout the wiki which shows only very specific sets of markers such as trails with a certain region or above a certain elevation.
Another issue is that the wiki will eventually contain thousands of trails, so the maps need to load the trail location data after the page has loaded, and the popup boxes in the markers need to load their content on-demand too.
Contents
- 1 Semantically annotating the infobox template
- 2 Retrieving the location data via AJAX
- 3 Creating a custom popup box using the overlay method
- 4 Populating the popup box with data via AJAX
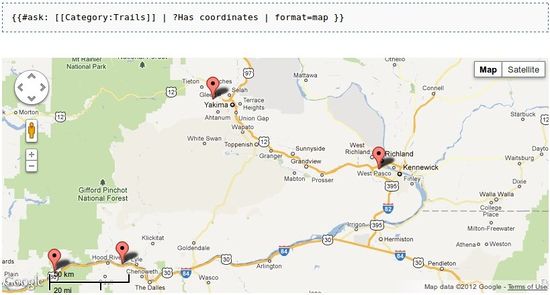
- 5 Selecting markers with SMW queries
- 6 Finishing up phase one
- 7 Marker clustering
- 8 Filter form
- 9 Caching
- 10 Current TODO
- 11 Later (maybe)
Semantically annotating the infobox template
|
|
Retrieving the location data via AJAX
Creating a custom popup box using the overlay method
I started with this script from the exampled in the Google documentation.
Populating the popup box with data via AJAX
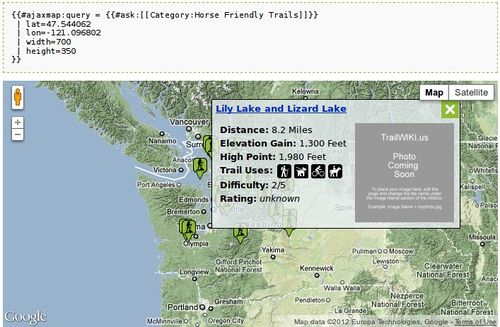
Selecting markers with SMW queries
This was achieved by allowing a query parameter to be added to the #ajaxmap parser-function that contains a SMW #ask query (or in fact any other kind of query that produces a list of title links as a result such as DPL). These article titles are then extracted out of the resulting list and included in the ajaxmap_opt array defined in the JavaScript for that map. The JavaScript Ajax request then includes these titles in its query parameter when it asks for the location information.
This is not perfect because the list of titles should not have to be sent to and from the client, it would be better for the Ajax request to send just an identifier that the PHP can use to perform the #ask query then rather than performing it when the parser-function was first expanded.
Finishing up phase one
Marker clustering
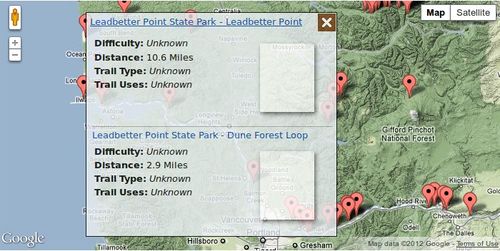
A new requirement has been added to help speed up the rendering of the maps with many markers. The idea is to combine markers that are very close into a single cluster that works similarly to the markers that are in identical positions (due to multiple trails starting at the same location). The proximity is in terms of pixels though, not geographic distance, so the clustering depends on the scale.
A function would be added which transforms the location data (an list of geographic locations, each containing a list of trail titles) into a new list of the same format, but with the geographic locations merged if their current pixel distance is less than a certain amount. There should really be an additional array of pre-defined named-regions that could be made to apply above a given scale. The region title would be used in the title bar of the popup box instead of the first trail title.
This function to transform the data that the markers are based on would be called when the data is first collected, and again whenever the scale changes. The function needs to detect which markers are affected and create/delete them to match the new locations table. It would do this by creating the new data in a temporary table, then updating the markers by comparing the new transformed table with the last transformed table and then making the new table current.
Another useful addition would be to allow this transform to separate out the trails that start at identical locations into a circle so they can be seen separately at a small enough scale.
Before actually starting to write the clustering, lets check what's already been done ;-)
These clusterers don't really do quite what we want - they're grid-based for one thing. I think the best way would be to get the PHP to handle the clustering and cache the data (and may as well cache the query lists along with it). The cluster cache can be invalidated when new location data is saved, and the query data whenever any trail data is updated.
Custom markers with numbers
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2436484/how-can-i-create-numbered-map-markers-in-google-maps-v3
- http://gmaps-samples-v3.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/overlayview/custommarker.html
- http://www.evoluted.net/thinktank/web-development/google-maps-api-v3-custom-location-pins
- http://code.google.com/apis/maps/documentation/javascript/overlays.html#ComplexIcons
- http://code.google.com/p/google-maps-utility-library-v3/wiki/Libraries
- http://google-maps-utility-library-v3.googlecode.com/svn/tags/markerwithlabel/1.0.1/examples/lettered.html
- http://www.geocodezip.com/basic8j.asp?filename=example_number.xml
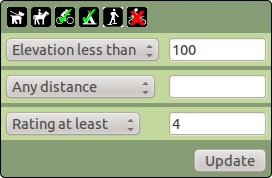
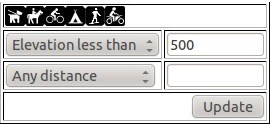
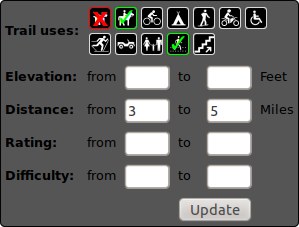
Filter form
A filter form has been added so that, if enabled, a form is available that allows users to tick or un-tick options such as "Dog friendly", or specify parameter ranges such distance or elevation, and the markers will be added/removed dynamically to match the query.
|
|
Caching
Obtaining the location data for many hundreds of trails takes 10-15 seconds to return from the server. This is because the data for each trail needs to be extracted from the wikitext content of each trail article. So to speed this up, an SQL table was created to cache the location data. The getLocation method first checks if the requested trail has its location stored in the cache, and returns the data straight away if so. If not, it then calls the more expensive getTrailInfo method which reads the article and extracts the data from the wikitext content.
The cache system has to tie into a couple of hooks so that the cache can be updated when trail information is created, deleted, or modified. The RevisionInsertComplete hook is used to detect if newly saved revisions have create a new trail or made any changes to the location of an existing trail. Both this hook and the ArticleDeleteComplete hook also do a general check to remove any location data from the cache that no longer has a corresponding trail article in the wiki. This could occur from articles being deleted or trail infobox templates being deleted or overwritten.
The trail location list now returns the data in a fraction of a second even for many hundreds of trails. It could still be improved more by making use of the modified HTTP headers to tell the client that it can locally cache the data and check the modified header to check if the entire data-set needs to be transferred.
Current TODO
- Change the markers for clusters to custom markers having the number of trails shown
- Disable clustering and zoom > 8
- The filtering should be applied to the total trails before the clustering is applied because its less expensive
- The filtering should be stored in the map-opts as current_filter rather than as a parameter in updateMarkers
Later (maybe)
- Store article lists from ask queries in DB so the lists aren't sent to and from the client
- Store the icon paths in the JS so they're not sent to client
- Image links can be made more effciient since they double-up the name and include a constant "140px"
- Cache all trail data, not just location data
- Use HTTP "modified" headers to reduce data-transfer of trail info