Wiki Organisation
Many organisations and projects are using wikis for more than just their content management needs. The wiki environment also works very well as a project management system due to it's inherent collaboration and auditing facilities. A basic wiki installation can be used for this by adopting working conventions that all of the wiki users in the organisation are familiar with and can refer to when necessary.
To be able to use a wiki in this capacity it is important that all the users take the advanced wiki training session which covers categorisation, article history, watch-lists, permissions and portals. With these skills the users can document their standard procedures and work on jobs together in accordance with a model called the blackboard metaphor. This is how the administrators collaborate on work together for the Wikipedia online encyclopedia project which the MediaWiki software was created for.
The blackboard metaphor is a very good system for users who are scattered around the world in different time zones, speak different languages and work casually in their roles whenever they have time available. But for organisations working on an intranet together their needs are often more complex and dynamic, requiring tight schedules, records and reporting and a generally higher level of structure. This could still be done with a basic wiki installation and the blackboard metaphor, but would require extremely well defined practices and a very high level of skill from all the users. This is where our concept of "wiki organisation" enters the picture.
Contents
The Organic Design Package
At Organic Design we've been developing a "wiki organisation package" for the last few years which extends the basic wiki functionality to allow for an arbitrary level of complexity in terms of the organisational system that can be run in the wiki environment, while requiring the users to undergo only a few hours of additional training.
The wiki organisation package essentially offers the ability to have a custom made application created within the wiki environment which can even be modified by the users themselves after they've become familiar enough with it. This "collaborative application" aspect gives it a huge advantage over the standard desktop application paradigm, but on top of this, every change made to the application or any of the work being carried on within it is fully auditable and reversible since it's all part of the wiki's content which inherently comes with full history.
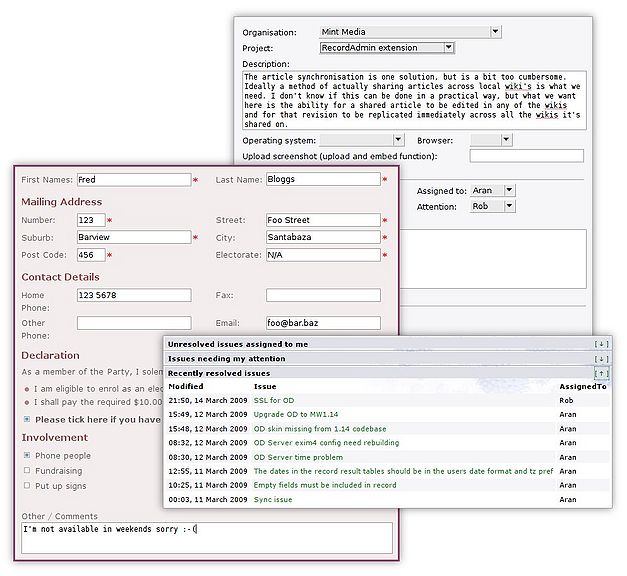
Even our basic installations come with all the wiki organisation extensions at no additional cost, but to have the structured content fully implemented for your organisation can take a lot of work to initially set up depending on the complexity of the aspects of your organisation you wish to model. The image below shows a few examples taken from wikis currently using the wiki organisation package.
We are pursuing the vision of a generic organisational framework composed of people working together in a specific unified way, which we shall attempt to describe in this article. Wiki Organisation is a good step in the right direction toward this vision but it is important to understand that we are not talking about a specific technology here, but rather a way of working which can be encapsulated by, or implemented within almost any collaborative environment. The definition of this system undergoes continuous refinement as we use it to organise and manage our own jobs and projects. There are a number of top-level aspects to this way which we call classes. The whole system is encapsulated in an overall tree structure which we call the Organic Ontology, eventually we hope for this structure to be defined to the extent that a complete description of the system can be exported in an official ontology language such as OWL.
Wiki Organisation Extensions
We include many extensions in our standard wiki installations (included in the GeneralExtensions.php file). Our organisational system is dependent on most of these for its functionality. However most of them do not need to be discussed here as they offer technical functionality such as additional magic words etc which, while important, don't contribute to the high level concepts of the system. Following is a brief description of the key extensions contributing to the wiki organisation concept.
RecordAdmin
CategoryWatch
DynamicPageList
Organisational Model
Note: this section still needs expanding The basic structure of the generic wiki organisation system is an ontology representing the organisation as a whole. The organisation is divided up according to its departments/divisions and/or roles and maybe into various branch offices etc. We then have a number of classes which are the aspects such as resources, people, places, procedures and best practices which appear in various places throughout that tree. The individual items contained within the occurrences of the classes throughout the tree may change dynamically as work flows through the system and are made accessible through department/role portals which have specific information as well as creating a dynamically queried portlet for each of the classes within its context. The ontology is shown in the wiki's sidebar tree and goes down to the level of the classes within the departments/roles, the dynamic items within those are only shown in the portals which are linked to from the department/role nodes in the tree.
- Generic framework: A Generic framework or environment that encapsulates information in a structured way. By generic here we mean that it can be implemented with nothing more than linking, categorisation and transclusion - basic functionalities which are available to any reasonable content environment. An Organic ontology.
- Software unification: Software unification though connectivity of diverse applications.
- System documentation: If the roles, projects and procedures are fully documented then you can change any aspect of a system, for example move the framework to a different software platform or incorporate a new application into the system.
- Technology independence: The collaborative nature and completeness of the documentation allows independence from any specialist support or and specific technology
- Reproducibility: Reproducibility of systems the current work/research conducted without relying on specialists.
- Allows dynamic expansion of systems
- Mitigates against any potential disasters
Wikipedia and Mediawiki
The goal of a wiki is to provide an environment where the collective intelligence of all the users of the software is harnessed. We chose to use MediaWiki for our collaborative environment for a few critical reasons
- It is the successful software behind Wikipedia providing a familiar interface to users and ensuring it will last for some years to come
- It has proven itself as a highly scalable framework
- The software is undergoing very active and organised development
- The content management and workflow policies provide an excellent example of how to collaborate effectively
- The content itself is extremely re-usable and useful
The Wikipedia project contains millions of articles which are collaborated on by millions of users. At any one time there are thousands of threads of work underway, all being carried out by thousands of administrators. Its this underlying structure of administration consisting of roles, policies, categories, procedures and jobs that allow the content to evolve over time into a more and more presentable, objective and concise state. All of this administration is achieved using the same article environment as the main content uses so that the system itself is able to evolve under collaboration.
In a collaborative and dynamic environment, documented procedures can also include associated resources and information that are required in their day-to-day application, and articles can contain the current state of specific jobs and projects including discussion, planning and research. This means that the documentation for each role, procedure, project or any other entity within the organisation forms a natural communications channel, because the attention of those that work within those entities is focussed there regularly in day-to-day operation.
MediaWiki Organisation
In the last couple of years there has been a massive increase int the use of MediaWiki software within private LANs and corporate intranets. In these environments MediaWiki is being used to document work and procedures and discuss ideas and plans.
The modern concept of an organisational system is ideally suited to a wiki environment. For example a category-based workflow model like Wikipedia use is essentially a simple means of implementing the blackboard system. Semantic MediaWiki in conjunction with Semantic Forms brings a new level of "web3" structure to the article environemnt. By combining this structural aspect with a spreadsheet-like way of selecting lists of structured articles and editing their proeprties, the wiki environment will be able to support a flexible system of organisation encompassing workflow, scheduling and automation and will be able to integrate more tightly with foreign applications.
The specific structure we have in mind is to structure the workflow categories as a tree of organisational activity which covers the whole organisation for example
- organisation → departments → roles → procedures
This is the tree of active working components from highest to lowest scale. Each of these components is represented by an article which acts as its "home page" and contains dynamic lists of their current work, research, messages and other specific resources. Instead of being viewed in the style of a category page, workspaces are more appropriately rendered as a list like a spreadsheet or email inbox, the items of which can be sorted, filtered, queried and properties edited in-place, including mass-updates.
The Wiki Organisation package
Using the Set up a new organisational system procedure a group can set up a network of workstations and servers along with a wiki-based organisational system with which to manage and utilise them. Each trust-group of servers and workstations form a shared file-system within which all their data is stored so that a robust and resilient infrastructure of knowledge can be maintained by all groups transparently.
The package includes installed applications for use on workstations as well as a server running a wiki containing the template organisational system of procedures and practices which can be modified to suit an organisations specific needs. Also included is a full email solution with spam protection, IMAP folders and webmail and also basic accounting and scheduling/booking needs are handled.
The package automatically stays up to date on all workstations and servers so that the system as a whole can continue to evolve as we refine and develop it.
Template wiki
The wiki supplied with a wiki organisation package is still being developed and will be in the form of a collection of articles, images and extensions. The articles are collected in export form and is initially available at wiki article packages. As well as the standard sets of templates it should also include the following defaults.
- Main page should be a more specific and helpful portal
- An welcome message should be emailed to users once the new wiki is set up guiding them to the user setup procedure
- Preferences should already be set up to email watched pages
- CategoryWatch should set some cats automatically based on role
Lessons Learned
Our first attempt at developing an organisational framework based on Mediawiki software was a Fork of MediaWiki 1.4 called XmlWiki. The approach utilized a Properties namespace which worked in a similar way to the discussion pages such that any article could have an associated properties page. Using the properties page, permissions could be set on articles, and formatting/language control and other functionality were provided. This project abandoned in 2006 in favour of an extension based approach, but some important lessons were learned along the way.
Separating Content and Implementation
One of the most important reasons why we abandoned XmlWiki is because it separated the article properties into their own article and syntax, rather than using the wiki's existing ability to describe parameters using standard template functionality. Another reason we abandoned it was when we realised that Semantic MediaWiki was a far better approach than a separate article. But we can still apply this lesson to how we implement semantic annotations.
If our approach requires us to add and edit these annotations directly within the article content, we are locking ourselves into a particular syntax and technology. Instead, such properties should be added to an article by embedding a template with the properties supplied as named template parameters. The specific syntax of the semantic annotations or parser-functions are then centralised into the template definitions rather than in the many articles that use them.
WYSIWYG and Forms
Many people think that the out-of-the-box absence of a WYSIWYG editor is the main reason that wikitext is considered difficult, but in our experience the main difficulty beginners have is with categorisation and templates, not the basic formatting. The best idea would be to use WYSIWYG editors to handle all wikitext except for template syntax which is handled with a forms solution. The Semantic MediaWiki and Semantic Forms combo handle this well, but need to be extended to work with MediaWiki API and AJAX.
During 2008 the RecordAdmin extension was introduced into our system which allows simple form-based handling of templates. They can be treated as records so they can be searched for based on parameter vaue, and edited via their corresponding form. Rather than using specific syntax, RecordAdmin allows standard HTML-based forms to be used so that there is little learning required for anyone already familiar with standard HTML.
System Administration
Part of the workflow system must include the jobs which keep the best practices up to date and ensure the roles are following it. An administrative role can be added which includes procedures for ensuring the best practices are up to date and being followed properly. Since all the entities receive regular attention from those working within them, it means that when changes need to be applied to procedures or discussion about solutions need to take place they won't go unnoticed.
Current Work
We currently maintain our own procedures in a wiki which include maintaining servers and workstations with their OS and software requirements, working on various IT projects and collaborative research and development for our own projects. We've been chipping away at a number of extensions aimed at enabling us to implementing the wiki organisation ideas more fully.
- ListView - spreadsheet-like list selection and editing
- SimpleForms - upgrading to work with Semantic Forms and API
- Extension talk:SimpleSecurity4.php - implementing a reliable permissions system
- Selenium - automation of testing functionality
- Packages - a package mechanism for maintaining and distributing collections of articles
Automation
Automation plays an important role in any organisation, especially those involved in IT. Part of our current system is a robot framework which allows us to schedule backups, content maintenance work and functionality tests. Since robots integrate with the system as normal users, they will be able to form a part of the same workflow as the human users. As procedures become more refined they can eventually be specified formally and automated, and when automated procedures fail, they can then easily be temporarily handled by users.
Distributed
Another thread of work we've been chipping away at is MediaWikiLite which is designed to run using the SQLite shared library instead of large database server software like MySQL. MediaWikiLite will eventually be able to run as a daemon or service without requiring a web server. MediaWikiLite can easily be installed on any small workstation and even on an iPod-touch or iPhone, it goes hand-in-hand with the P2P extension which is aiming towards a distributed serverless model that can synchronise content with trusted peers. It's important to note that this functionality is not a fork of the software, its a MediaWiki extension and we've added the SQLite support directly to the code-base of MediaWiki 1.13.
Road Map
Our next step is to use MediaWiki in conjunction with a handful of extensions such as Semantic MediaWiki and ListView, to encapsulate a range of generic organisational concepts as described in the following section. We will continue to develop this further toward the idea of a generic organisational framework in tandem with applying the technology to create actual, functioning organisations within the Organic Design Wikia, with people collaborating to create content, setting up workflows or refining procedures.
The main work we'll be doing apart from completing the extensions currently under way, is to make the system description more complete and more re-usable. The Packages extension mentioned above will allow us to maintain and distribute large sets of template articles and pre-populated structures of categories and content.
A new feature in MediaWiki is the API which allows it to integrate much more easily with foreign software. many of our extensions use AJAX functionality to request and manipulate wiki content dynamically without page reloads. The MediaWiki API makes such functionality more secure and efficient. The API layer also makes automation far more efficient by enabling the Robot framework to integrate directly with the MediaWiki system rather than via the HTML forms interface which is really designed for Humans.
Self containment
A key feature of this way of working, which MediaWiki software (in terms of functionality) and projects like Wikipedia (in terms of application) exhibit, is that the content (in the case of Wikipedia, the actual content articles and categories) as well as the administrative and organisational mechanisms (Wikipedia: User administration, policy documentation, deletion or article improvement workflows, etc.) are described in the same collaborative environment, giving rise to a basic form of self containment.
The reason we chose MediaWiki is because in addition to fulfilling our basic technical criteria, it is being used to run Wikipedia; therefore we're working with a large and active community, the code is well-tested and under continuous development, and has proven scalability. We also agree with the philosophy of Wikipedia's parent organisation, the Wikimedia foundation, and their statement: "Imagine a world in which every single human being can freely share in the sum of all knowledge. That's our commitment." By using MediaWiki, we are aligning ourselves with that philosophy, the development momentum, a large amount of people familiar with the software interface and a vast amount of freely accessible content and knowledge.