Set up a Cardano ITN staking pool
To run a staking pool you'll need a reasonable server that is on a reliable high-bandwidth connection. First you need to install the node software, then create the cryptographically signed staking pool parameters associated with a funded pledge address, and then finally register your pool so it shows up in the staking wallets. This section is mainly based on the instructions at Stake Pool Operators How-To with a few differences.
Contents
- 1 Install and configure Jormungandr
- 2 Keeping your node running with a sentinel
- 3 Creating and funding a reward address
- 4 Create the stake pool and publish to the blockchain
- 5 Backup your pool data
- 6 Start your pool!
- 7 Register your pool in the official registry
- 8 Monitor your pool's rewards
- 9 See also
Install and configure Jormungandr
We start by installing the latest release (not a pre release) of Jormungandr from the official repo (it's a good idea to subscribe to the repo's feed so you can know as soon as new stable releases are available). One important difference from their procedure is that we need to use the itn_rewards_v1 configuration rather than the beta configuration. A couple of differences from their procedure too: first I had to change both 0.0.0.0's in the config to my external IP not just the public one, second a storage location needs to be added to make the chain data persistent. The first few sections of your config file should look something like this:
{
"log": [
{
"format": "plain",
"level": "info",
"output": "stdout"
}
],
"storage": "./storage/",
"p2p": {
"listen_address": "/ip4/1.2.3.4/tcp/3100",
"public_address": "/ip4/1.2.3.4/tcp/3100",
"topics_of_interest": {
"blocks": "high",
"messages": "high"
},
. . .Another issue is that I was not able to find any genesis hash in the configuration as it says there should be, I had to obtain it myself from the last page of slots for epoch 0 which yields this (later I found this parameter and others here). It's best to put this genesis has into a file called genesis-hash.txt so that it can be referred to easily from other programs when needed.
I created a script called start.sh to run it with the correct parameters in the background and redirected its output to a log file:
#!/bin/sh
nohup ./jormungandr --config itn_rewards_v1-config.yaml --genesis-block-hash `cat genesis-hash.txt` >> debug.log &If you see no errors in the log and the daemon keeps running, you can check the sync progress by running the node stats command and checking that the lastBlockDate matches the current epoch and slot shown in the Shelley explorer.
./jcli rest v0 node stats get --host "http://127.0.0.1:3100/api"blockRecvCnt: 41
lastBlockContentSize: 0
lastBlockDate: 7.35623
lastBlockFees: 0
lastBlockHash: "f78c64c030383899ebb1b25dac7ae9d360d222d0b80320323375dc51762651d2"
lastBlockHeight: 26342
lastBlockSum: 0
lastBlockTime: "2019-12-21T15:15:20+00:00"
lastBlockTx: 0
state: "Running"
txRecvCnt: 45
uptime: 886
version: "jormungandr 0.8.3-8f276c0"To shut the node down gracefully use:
./jcli rest v0 shutdown get --host "http://127.0.0.1:3100/api"Keeping your node running with a sentinel
This may be just a problem on the testnet, but nodes seem to get stuck a lot and require a restart. This used to happen a lot with Masternodes as well, and the general solution was to run a "sentinel" script that checks on the node and perform the necessary processes when something's not right. In the case of Jormungandr a simple restart of the node seems to resolve the issue, so I made this sentinel.pl script that is to be run from the crontab every minute. It checks if no new block hash has been created for more than a certain time, and if not it restarts the node. If it's still stuck on the same block even after restarting, then the node has probably gotten itself onto a fork, so the sentinel backs up the chain data and logs and restarts the node from a clean slate.
The script takes two parameters, the first is the number of seconds to wait between polling the node (must be a multiple of 60), and the second is the number of seconds of seeing no new block hash after which we should assume that the node is stuck and restart it. Both parameters are optional and default to 5 and 120 respectively. The script assumes a local node to be running on port 3100, and also expects a script called start.sh in the same directory that starts the node in the background with all the necessary parameters.
The script writes the situation to a file in the same directory called sentinel.log which will look like the following snippet. The first part in square brackets is the Unix timestamp of the entry followed by a duration after the slash.
[1577145836/040] Epoch:10 Slot:8709 Block:34597 Hash:7c1db1bbb77d88636349371d5e7ef60e3cb8a2257e2d9aa8d109eecce3236689
[1577145891/055] Epoch:10 Slot:8735 Block:34598 Hash:fb84bb2a0e48233837d1d5773219b3be9661f333f3aaea41867372f0ed224197
[1577145916/025] Epoch:10 Slot:8746 Block:34599 Hash:c3da1a7f72815280f70e1956b33fda993ad788317515dbd2a5c74e96293b5c2b
[1577146041/125] Stuck on 10.8746, restarting node...
[1577146046/000] Status unknown, check if the node is running!
[1577146051/030] Bootstrapping
[1577146086/000] Epoch:10 Slot:8821 Block:34600 Hash:c93189408bcf7e9fe954e72502f720b661002fb365c3283b16b0a8260bd2cf4f
[1577146126/040] Epoch:10 Slot:8854 Block:34601 Hash:c3af8796c932f635067757b4cbaa1c58c6e7623d1660902172f0cf59b439d12e
[1577146136/010] Epoch:10 Slot:8858 Block:34602 Hash:b21af406419002e5b57b7e3bee7dec5378d10f76670d7780a642fbe1d2e60082
[1577146167/031] Epoch:10 Slot:8872 Block:34603 Hash:573c2b9142eff7435d2aa1cd657b808546c592c62e3710d0143670032ad0feccNote1: The sentinel misses blocks that are generated quicker than the polling period, so the log shouldn't be used as a definitive chain report, for this application it's only the slow updates that we're concerned about, so missing blocks are not a problem.
Note2: If you're signed up with pooltool.io and have claimed your pool on the site, you can supply your user ID as the third parameter to the sentinel script, and it will share your node's block height with the site so you can see easily if it's up to date on the PoolTool site, as shown below in the green bubble to the right.
By providing your block height to PoolTool, they will return the current maximum height across all shared heights they've received, which allows your sentinel to show how far behind your node is. This is shown as a negative integer appended to the block number in the log as shown in the example below, most of the blocks should be appended with "-0". Sometimes you'll see block heights appended with "--" which means the request to PoolTool failed for example due to taking longer than the 1s timeout limit imposed by the sentinel script.
[1577918246/109] Epoch:19 Slot:6085 Block:62588-2 Hash:7f0ed4a88a80104aea8e9162fe618b6f8d3d480773dd94eb3b66729c9bdd4c7bCreating and funding a reward address
Now we need to create three files for our reward account, a public/private key-pair and it's corresponding ADA address which I did by following the instructions in how to register your stake pool on the chain.
./jcli key generate --type ed25519 | tee owner.prv | ./jcli key to-public > owner.pub
./jcli address account --testing --prefix addr `cat owner.pub` > owner.addrYou can then send funds (minimum 510 ADA) to the address in the owner.addr file from Daedalus or Yoroi, and then check the balance:
./jcli rest v0 account get `cat owner.addr` -h http://127.0.0.1:3100/apicounter: 0
delegation:
pools: []
last_rewards:
epoch: 0
reward: 0
value: 550000000Create the stake pool and publish to the blockchain
Finally we need to create the stake pool itself which can be done by calling the handy createStakePool.sh and send-certificate.sh scripts. You only need to run the former script which calls the latter, make sure both are executable first. The script takes four parameters, the listening port, the fixed tax (in lovelace), the percentage as a fraction and the private key of your reward address that you put in the owner.prv file above. For example:
./createStakePool.sh 3100 1000000 5/100 OWNER_PRIV_KEY | tee results.txtThis will create a pool that takes 1 ADA (1M Lovelaces) fixed rate, and 5%. Note that the instructions say you need another tax_limit parameter, but this must have been removed at some point. This script returns two important values that you need to keep, the Pool ID and Pool Owner, but by appending the tee command, all the output is also captured in results.txt. It also creates the important node_secret.yaml file that is used when starting jormungandr from now on. Check the output for errors and successful signing and sending of the new pool registration transaction, you should see something like this in your output:
## 10. Encode and send the transaction
56ded95ea6868470337272ef899264abb5c27dcdd2f9aae839924dca19b5dd3f
## 11. Remove the temporary files
## Waiting for new block to be created (timeout = 200 blocks = 400s)
New block was created - 8fe7ac108640778ca53ce4d38ed8b7b6092454770d4aaf04a38ec548cc66b330Note: If anything goes wrong in this process, you're best creating a new pledge address before trying again, because if you end up with more than one pool operating on the same pledge address, only the last one will work.
Backup your pool data
IMPORTANT: As soon as you've created an address and node secret, create a directory for it using the stake id, or its first few characters, as the name and copy all the specific files into it so you have them in case you need them later. For example you need them if you want to retire the pool, or sign any messages as that pool owner, even if it's just a dummy run and you're sure you'll never need to refer to them again, do it anyway! The files are:
- node_secret.yaml
- owner.prv
- owner.pub
- owner.addr
- stake_pool.id
- results.txt
If you ever need to rebuild your pool, for example if you need to move server, then simply put these files into the directory after you've put all the program files and scripts in place and then when you run jormungandr it will start as that pool and retrieving the block chain data.
Start your pool!
Now you're ready to shut your node down and restart it with you secret key parameter to start it as a pool!
./jcli rest v0 shutdown get --host "http://127.0.0.1:3100/api"
nohup ./jormungandr --config itn_rewards_v1-config.yaml --secret node_secret.yaml --genesis-block-hash `cat genesis-hash.txt` >> debug.log &Note: Remember to add the --secret node_secret.yaml parameter to the command in your start.sh script.
Register your pool in the official registry
To allow people to delegate their stake to your pool in a supporting wallet, you need to add your pool to the public registry. This is done by creating a JSON file containing your pool's details, and a file signing the JSON content with the owner's private key, and committing these files to the registry's Github repo.
The name of the pool is your owner public key from the owner.pub file appended with a .json file extension. The content of the file is as follows. The "owner" field is the same key as used in the filename, and the "pledge_address" field is the owner address from the owner.addr file.
{
"owner": "OWNER_PUBKEY",
"name": "Pudim o gatinho com fome",
"description": "All your stake are belong with PUDIM!",
"ticker": "PUDIM",
"homepage": "https://pudim.od.gy",
"pledge_address": "OWNER_ADDR"
}Note: This file must be valid JSON (e.g. you must use double quotes) otherwise the pull request will fail.
Then to sign this JSON file with the owner's private key, you use jcli as follows:
./jcli key sign --secret-key owner.prv --output `cat owner.pub`.sig `cat owner.pub`.json
You then need to fork the Cardano foundation's incentivized-testnet-stakepool-registry Github repo, clone your new fork of it, add your two files into the registry directory, add, commit and push them and then create a pull request on the Github site in your forked repo page. Note that it's always best to create a new branch for a pull request, because all commits even after you've made the request are automatically included in the pull request at the upstream repo. Note that the following example is assuming that you've cloned the repo in your pool directory, if you haven't adjust the path to your keys as necessary.
git clone git clone git@github.com:YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME/incentivized-testnet-stakepool-registry.git
git checkout -b PUDIM
cd incentivized-testnet-stakepool-registry/registry
cp ../../OWNER_PUBKEY.* ./
git add *
git commit -m "PUDIM"
git push --set-upstream origin PUDIMThe pull request will verify your that your JSON is valid and your signature verifies, and if so the team should approve it for inclusion in the registry shortly after, and your stake pool will be listed in the delegation interface of Daedalus!
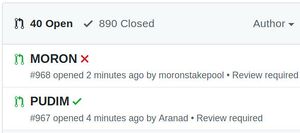
The image below shows two pull requests to the official registry repo, our PUDIM registration has passed, meaning that the JSON syntax is all correct and the signature has been successfully verified, but the MORON pool registration has not been successful. Even after a successful pull request, manual validation is required by the Cardano team, ours was accepted the next day.
Note: If you want to remove your pool from the register or change it's details, see these details which involve creating two pull requests, one for a signed "voiding" of the old metadata file, and another to add the new metadata and signature files.
Congratulations PUDIM! She produced her first block in the early morning of December 27th 2019 🎉 🎉 🎉
All blocks produced by PUDIM can be seen in the Shelly Explorer here.
Monitor your pool's rewards
For smaller pools like PUDIM that only produce a few blocks per epoch, it can be nice to receive and email each time a new one is produced. Of course for the bigger pools this would be one hell of a nuisance, because you'd be getting notified every few minutes!
I've made a script for this called cardano-pool-blocks.pl which uses the official IOHK testnet block explorer and registration repo to get the information on the blocks your node has created, and to get your node's metadata to make the message more friendly.
The script is called with two parameters, the first being the email address to notify, and the second being the ID of your stake pool (as shown in the stake_pool.id file). It will create a log of the created blocks in the same directory called cardano-pool-blocks.log. It should be called regularly on the crontab and will send email such as the following example after a new block is made. I've highlighted the parts that come from your registered metadata.
PUDIM has produced a new block!Congratulations!!!
This is the 18th block produced by Pudim a gatinha com fome!
Epoch:17 Slot:36049 Block:58639
Hash:6d5f133d01221117b2bb2b5ee4c042588c679eaeab10d83e40f5e7c0cc902a3c
All your stake are belong with PUDIM!
https://pudim.od.gySee also
- Cardano
- Pudim's Cardano staking pool
- staking.cardano.org
- Staking Design Specification
- IOHK blog: Stake pools in Cardano
- Emurgo blog: Features of Cardano staking
- 7 part lecture series on the Cardano incentives and staking mechanism
- PoolTool.io & ADApools.org
- Useful resources for operating stake pools